In the realm of innovation, artificial intelligence (AI), especially generative AI, stands out as a monumental force that is redefining industries. The profound transformative impact of this technology is enabling organizations to generate novel content like text, images, and music. However, they need to be aware of the ethical considerations at play.
Generative AI is accelerating and amplifying content creativity across media, marketing, and other sectors, as well as providing enhanced and personalized healthcare treatment and adaptive style learning and education.
Despite generative AI's extraordinary capabilities, organizations have been facing serious ethical concerns surrounding data privacy, security, compliances, and policies. The technology also poses certain business risks for product engineering companies, such as threats to consumer privacy, data plagiarism, and misinformation.
Read more: A Deep Dive into Data Governance Frameworks
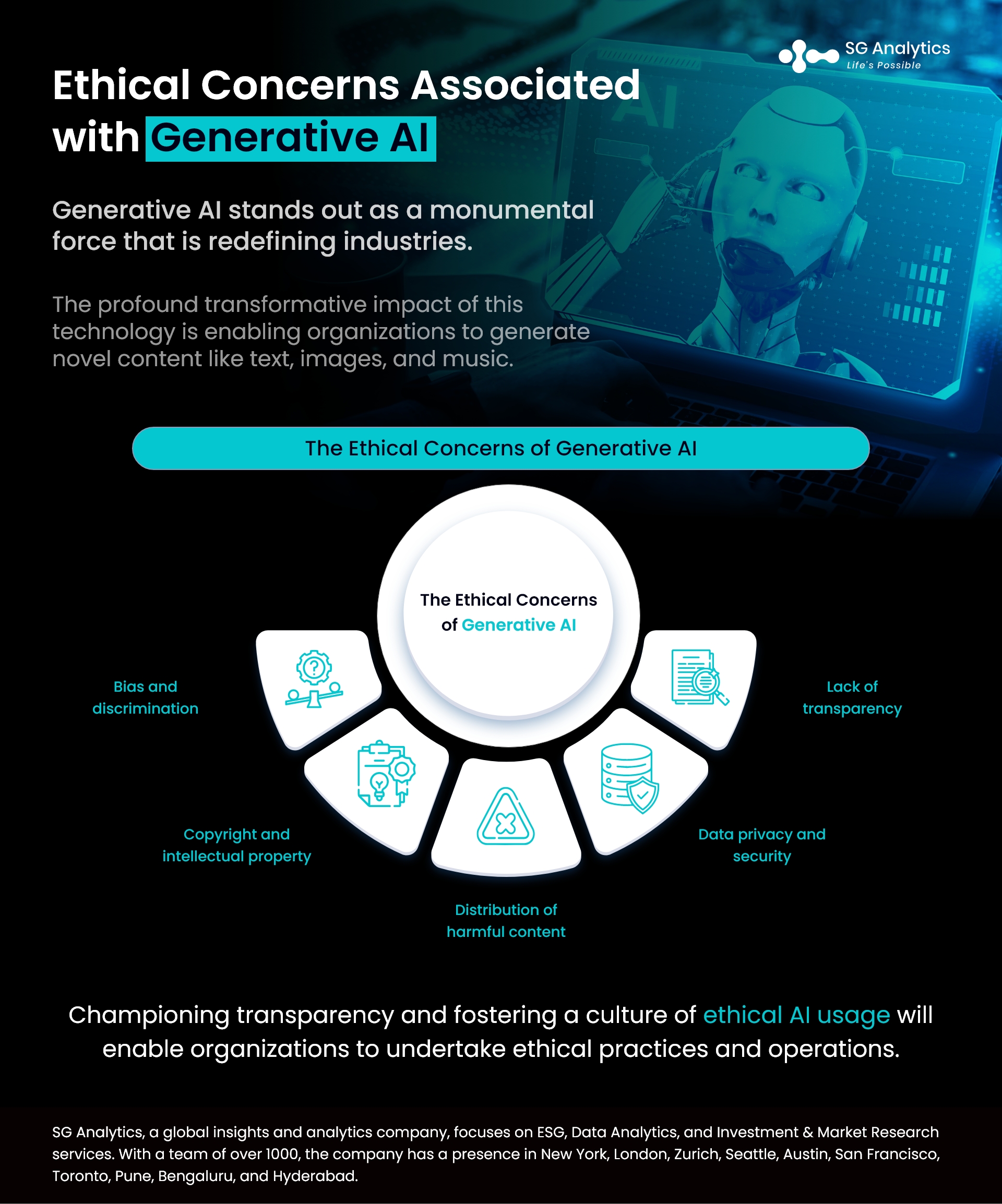
The Ethical Concerns of Generative AI
Let's explore some of the critical ethical implications that businesses dabble in generative AI, alongside some potential pitfalls and mitigative strategies.
-
Bias and Discrimination
Generative AI models mirror the data they are fed. Consequently, if trained on biased datasets, they will perpetuate those biases. AI that inadvertently perpetuates or exaggerates societal biases can draw legal repercussions and cause brand damage.
If the training data represents biases prevalent in society, the generative AI model will behave as per the fed data. It has, therefore, become imperative for organizations to fine-tune these generative AI models for specific tasks while adhering to the data privacy guidelines and ensuring that the biased data is removed from the model training.
Prioritizing diversity in training datasets and committing to periodic audits for unintended biases can help organizations integrate the importance of diverse training data. This will further help in ensuring that their generative models undergo rigorous bias checks and external audits.

-
Copyright and Intellectual Property
Generative AI models are trained on huge data sets. The ability of generative AI to formulate content that mirrors existing copyrighted materials further poses critical legal concerns. This can infringe upon the copyrights and intellectual property rights of other companies, leading to legal, reputational, and financial risk for the organization using pre-trained models. Intellectual property infringements result in costly legal battles along with reputational damage. It can also negatively impact creators and copyright holders.
Read more: 2024 Outlook: Generative AI and the Future of Work
Ensuring that training content is licensed and transparent will help outline how generated content is produced. The use of metadata tagging in training content will further help in tracing back origins, thereby ensuring transparent accountability.
-
Distribution of Harmful Content
While the ability of Generative AI models to develop human-like content assists organizations in enhancing their productivity, it can also help in generating damaging or offensive content. Generative AI tools like Deepfakes can create false images, videos, text, or speech and can be used as agenda-driven or to spread hate speech.
Automatically generated content can amplify the biases learned from the training data, resulting in biased or violent language. Due to this, such harmful content requires human intervention to align it with the organization's ethics.
-
Data Privacy and Security
Most of the concerns surrounding the use of generative AI tools are associated with data, including user privacy and generating synthetic multimodal data such as text, images, or videos.
Generative AI models trained on personal data often pose privacy risks. The unauthorized use of this data can cause synthetic profiles, which is emerging as a significant concern. A breach of data misuse or user privacy can lead to legal consequences and deteriorate user trust.
Read more: Navigating the Future of Technology Compliance with Blockchain and Data Privacy

Leaning towards anonymizing data when training models and strengthening data security measures will assist organizations in ensuring that their user data remains uncompromised. These systems require maintaining data assurance and integrity to avoid using biased data or data of questionable origin. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) principle highlights that only necessary data should be processed. Organizations must adopt similar principles to ensure that any non-essential personal data is stripped away before training.
-
Lack of Transparency
With AI systems, it is often difficult to understand how they arrived at a response or what factors help with their decision-making. The emergent capabilities of large models further amplify this gap.
Today, organizations are facing the issues of not only identifying additional emergent abilities but also trying to figure out why and how the systems try to predict unpredictability.
It is, therefore, the user's responsibility to dismiss the idea that all information available in the digital world can be trusted. And most of the problems can be solved by challenging and suspecting the available data. Fact-checking and verifying the authenticity of the data and its source of origin before using that knowledge will help nurture a transparent environment.
Read more: Why is Data Preparation Vital for the Successful Implementation of Generative AI
The Evolving Business Perspective and Way Forward
In this new world of generative AI, organizations leading from the forefront are carrying a weighty responsibility.
Generative AI holds immense potential to revolutionize different sectors - ranging from healthcare to education - by developing new content and enhancing productivity. However, this powerful technology also brings significant ethical concerns, such as the distribution of harmful content, copyright infringements, amplification of existing biases, and data privacy violations. This calls for introspection and ethical stewardship.
Beyond the societal and ethical implications, organizations are also facing tangible risks if they sidestep these issues. Brand image, user trust, and financial stability are at stake. Overlooking the ethical facets of generative AI today is nothing less than a business risk.
But with the world continuing to harness the capabilities of generative AI, it has become more crucial than ever to adopt these ethical best practices. And awareness is emerging as the key to getting generative AI right.
Awareness is the first step for organizations. By recognizing and understanding the ethical concerns associated with generative AI, organizations can proactively architect policies, processes, and strategies that promote responsible use. Championing transparency and fostering a culture of ethical AI usage within and outside the organization will further enable them to undertake ethical practices and operations.
SG Analytics, recognized by the Financial Times as one of APAC's fastest-growing firms, is a prominent insights and analytics company specializing in data-centric research and contextual analytics. Operating globally across the US, UK, Poland, Switzerland, and India, we expertly guide data from inception to transform it into invaluable insights using our knowledge-driven ecosystem, results-focused solutions, and advanced technology platform. Our distinguished clientele, including Fortune 500 giants, attests to our mastery of harnessing data with purpose, merging content and context to overcome business challenges. With our Brand Promise of "Life's Possible," we consistently deliver enduring value, ensuring the utmost client delight.
A leading enterprise in Generative AI solutions, SG Analytics focuses on unlocking unparalleled efficiency, customer satisfaction, and innovation for the client with end-to-end AI solutions. Contact us today to harness the immense power of artificial intelligence and set new benchmarks in operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and revenue generation.
About SG Analytics
SG Analytics (SGA) is a global data solutions firm that harnesses data with purpose across the data value chain - from origination, aggregation, management, modernization, and analytics to insights generation to create powerful business outcomes for its customers. Through its research and data analytics consulting services, SGA marries content with context to provide bespoke solutions to its customers, enabling them to improve efficiency, scale, and grow. The company has a presence in New York, London, Zurich, Seattle, Austin, San Francisco, Toronto, Pune, Bangalore, Hyderabad and Wroclaw. The firm serves customers across the banking, financial services and insurance (BFSI), technology, media and entertainment (M&E), and healthcare sectors, amongst others, including Fortune 500 companies.
Apart from being recognized by reputed firms such as Analytics India Magazine, Everest Group, and ISG, SG Analytics has been recently awarded as the top ESG consultancy of the year 2022 and Idea Awards 2023 by Entrepreneur India in the “Best Use of Data” category.